
Product Details
Constant Stress/Creep
In creep testing a constant extensional stress σ↓0 is applied at time t=0 and the subsequent Hencky strain is followed as function of time. The extensional creep compliance is defined as J↑Ε(t)=∈(t)/σ↓0 A large creep complience signifies a soft material, while a small creep compliance signifies a hard material. For viscoelastic liquids, the creep compliance ultimately increases linearly in time with a slope that is the inverse of the steady extensional viscosity.
|

|
|
|
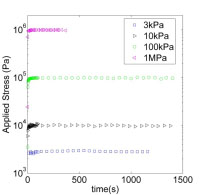
Extensional stress as a function of time for poly(methyl |
Creep compliance as a function of time for poly(methyl |
